The conventional wisdom is that beer is a local business. Despite many attempts, only a select few beer brands have made a successful transition from local to global. The stakes are high as those that win are viewed as the crowning success in the portfolios of the world’s best brewers. We have looked at the successes and failures of global brand building in beer, the market dynamics and best practices across FMCG, and we propose a four-step guide to build a successful global beer brand.
Published in “The Drinks Business” and available at www.thedrinksbusiness.com
Freddy Heineken, the grandson of Heineken founder Gerard Heineken, started his career with the family company in 1942 and became Chairman of the Board in 1971. Freddy was an eccentric man and a noted salesman who fell in love with American advertising and marketing. He was extremely focused on consumers, very hands-on and rightly credited with the creation of the Heineken brand “personality.”
When Freddy became Chairman of the Board, he pushed hard to expand Heineken beyond its local origins. What people often don’t realise is that Freddy did not have any formal marketing education. His approach was primarily entrepreneurial and instinctive. He did, however, understand that the Heineken brand had the potential to be unique among other beers and decided to put Heineken on the global map. His line of thinking was fivefold:
- Appeal to the young adult consumer
- Position the brand as premium and hip
- Create a green bottle with “export” on the label
- Craft a beer with superior and consistent taste
- Make it globally available
His experience in America helped him understand that a beer brand has to be unique to be successful globally. Freddy realised that in each market around the world there was a pocket of similar consumers that would drink Heineken, and he strove to reach them.
Although Freddy made a big difference in early days, his successors like Thony Ruys and Jean-François van Boxmeer deserve credit for developing a leading “export” business model that ultimately took the brand to over 170 countries, generating 25mHL of sales volume and premium pricing in most markets.
Amazingly, all this happened without an experienced professional marketer in the lead until the 2010 recruitment of Alexis Nasard as Chief Commercial Officer, who immediately made it his top priority to accelerate the brand’s growth and complete the “last mile” of the brand’s globalisation. Under recent leadership, Heineken has re-entered Interbrand’s Top 100 global brands at 91, the third ranked beer behind only Budweiser (29) and Corona (86). It stands alongside Coca-Cola (1), Pepsi (22), Jack Daniels (78) and Smirnoff (89) as a truly great global brand, and Alexis aims to have the brand as equally recognised as Apple, Google and Nike.
Today more than 75% of beer sales are still on local brands in every major country, and international brand volume represents only 11% of the global total. Why have so few other beer brands been able to achieve the same long-term, global success as Heineken? We spent the last six months trying to answer this question, and after a series of interviews and analysis we have uncovered four secrets to building a successful global beer brand.
We will share these shortly, but first, we look to the past to explain the mystery of the present.
Understanding the history of beer can help explain why beer brands have not been globalised like Coca-Cola and Pepsi
Beer has been sold in similar form and taste for thousands of years. Local tastes, high transport costs, short shelf life, availability of ingredients and packaging, taxes on imported alcoholic products, and impenetrable local wholesale networks have ensured beer remains a highly local product. As the wave of industrialisation followed by globalisation swept change through the world, the beer business evolved but largely remained local.
On the other hand, consumer goods companies like Coca-Cola and Pepsi are different. Free from the constraints of historical taste preferences, legacy systems, laws and infrastructure, they have been able to innovate and change across areas such as outlets, channels, distribution and packaging. Using one key brand, they grew their business with a global mind-set from the start.
The beer industry has consolidated dramatically over the last decade
In 1999, Coca-Cola and Pepsi together controlled almost 70% of worldwide soft drinks sales, whereas the top four brewers generated only 17% of global beer sales. Beer was viewed as one of the least consolidated, and least profitable, industries in FMCG.
Today the top four brewers account for 45% of global volume and over 55% of global revenue. The profitability of the beer industry has doubled (see Figure 1) because of greater scale, multiplier effects of reduced competition and the profitability of emerging markets. Despite this growth, beer is still an overwhelmingly local business. Brewers maintain local operations, local production and, most importantly, local brands.
Figure 1: Share of top four companies and industry EBIT margin
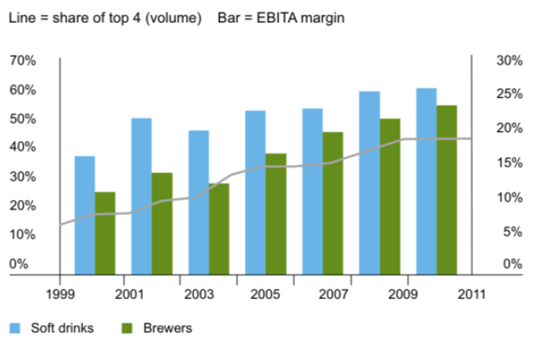
In local beer markets, brand consolidation is likely to continue
Beyond industry consolidation, brand consolidation brings further tangible and intangible benefits, including operational leverage, efficiency in advertising spend and increased consumer recognition. Companies with higher volume brands tend to be more profitable (see Figure 2)
Figure 2: Correlation between scale and profitability
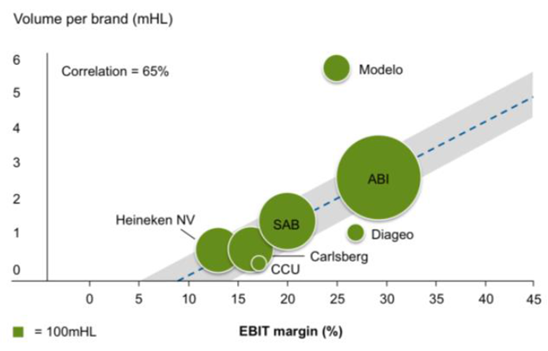
Brand concentration is slowly starting to occur across both developed and developing countries (see Figure 3). For example, the top five brands in China now represent 37% of the market, up from 12% 10 years ago. In the key African markets of Nigeria and South Africa, Star and Castel are leading the way, growing share at the same time as the growing market becomes more profitable.
Figure 3: Increasing share of the top five brands in local markets
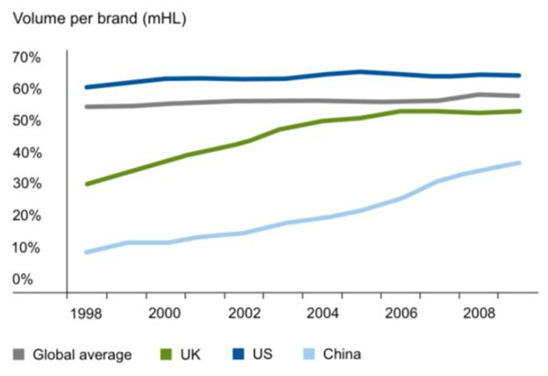
These trends toward both industry and local brand consolidation in beer, and historical trends across other FMCG industries, indicate the future is set-up for continued attempts to develop global beer brands.
Doing so is not obvious and requires a systematic approach and patience in your long-term investment. We have defined four key steps for getting there.
Step 1: Define the benefits of global brands to your organization
In our discussions with leading brewers, we found inconsistencies within and across organisations about the benefits global brands bring. Based on our experience they are:
- Leverage international media and advertising platforms: Only a global brand like Budweiser can take advantage of being the face of the FIFA World Cup.
- Better route to market: Premium international imports like Heineken and Corona are musts in the on-trade and off-trade.
- Consumer confidence: Being international makes you more credible; e.g., as Beck’s has expanded its footprint, it has also boosted awareness and credibility.
- Economies of scale: ABI and Heineken are saving 50% or more by producing one high-quality TVC instead of different TVCs for multiple markets.
- Repeatable and scalable model: Corona has expertly created a repeatable export model that takes into account each stage of a brand’s lifecycle in a country, so subsequent launches are increasingly effective.
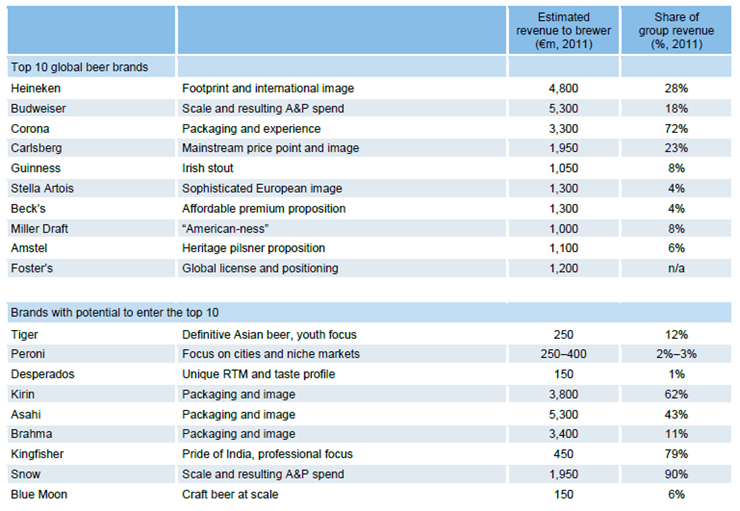
We identified the top 10 global beer brands (see Figure 4) as indicated both by the revenue, volume generated across multiple markets and the intent to be global (i.e., advertisement on global media platforms). Defining what a global brand means to your organisation is the first step toward success. It helps you set the governing objective for the brand, communicate the benefits of the brand internally and break down the “local prejudice” barrier that is still prevalent in the beer industry today.
Figure 4: Top 10 global beer brands
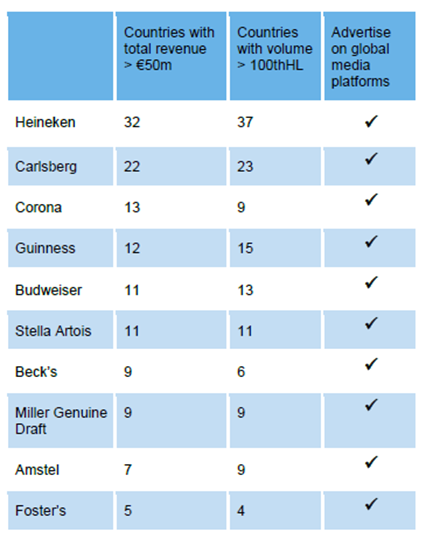
Exercise 1:
Define the benefits of global brands to your organisation.
Take the list above as a starting point and assess:
- The benefits of global brands to your organisation
- The implications of moving toward a global brand-led strategy
- The timelines for your project
|
Step 2: Identify the unique proposition and build a business model to support it
As we analysed hundreds of beer brands, it was striking to see that for those that had made the transition from local to global, there was no common reason for their success. What unites the eight global beer brands is that they have a unique customer value proposition and/or have an advantaged business model.
Building a unique customer value proposition
Through our research we consistently heard that to build a global brand you need great taste, local image and a brand that is currently profitable. We believe these factors were, and remain, critical to building a local but not global beer brand. Being very good in a number of areas is not enough to give a brand the front running in the global market. The starting point for selecting the right brand to take global is a unique customer value proposition.
Uniqueness means that there is a place in the mind of the consumers where your brand sits alone with clearly identified consumer “benefits”, ultimately driving strong buying behaviour and loyalty.
Why are taste and profitability not as important as a unique customer proposition?
Consumers are embarrassingly poor at differentiating between lagers in blind taste tests. A Carling study found consumers could not identify a significant difference in taste across five of its competitor’s lagers nor could they identify their favourite brand as having superior taste. Once labelled, the consumers immediately ranked their preferred brand as superior across taste factors.
Taste, to a large degree, is all in the eyes rather than the palette.
We also heard brewers should choose which brand to take global based on how profitable the brand currently is in key countries (with the idea being that if you are successful locally, you have a better chance of becoming successful globally). We believe that this will lead to the wrong brand being promoted on many occasions as profitability is a not a leading but a lagging indicator of the overall success of a brand.
Figure 5: Increasing share of the top five brands in local markets
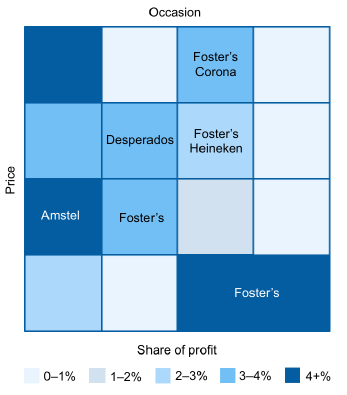
Figure 6: Global brands - uniqueness and value to their owners
Last, but not least, we need to emphasise the respective role of global trends versus local consumer insights. Although a brand with unique global potential needs to access universal trends (e.g., “coolness”), it has to nevertheless be able to appeal to specific consumer segments locally. Having strong insights on what the local consumer needs and buying behaviours are for key segments of the population is a crucial input for creating a unique global brand proposition.
We discovered that brands that fail to identify (and sustain over time) a material point of uniqueness on the global consumer map will fall into a negative cycle, slowly reducing volume and profitability in all markets over time. Unique brands are able to leverage their strengths to increase consumer appeal and grow rapidly.
Building a unique business model
It is not enough, however, to have a unique customer value proposition. A truly global brand also requires a business model that supports the brands uniqueness to reach its customers (e.g., privileged route to market, unique ability to engage new media, superior brewing scale).
Fifteen years ago, Foster’s looked like it would take the beer world by storm. It had secured global license arrangements, had a one-of-a-kind advertising campaign and tapped into the laid-back Australian culture of beach, barbecue and watching TV with mates. Volume has been steadily declining since 2005, including falling by 50% in the US (which it set out as a “priority market”).
What went wrong?
We believe that Foster’s suffered from confused positioning and lack of success in its home market. In the last decade, Foster’s has gone through multiple rebrandings, positioned itself across every price segment (from discount in Ireland and Australia to super-premium in Portugal and Italy) and has used varied RTMs from JVs, distributor agreements and its own operators, all of which had different priorities for the brand. Foster’s failed to drive success in Australia, meaning low visibility to tourists and no core to draw on to cross-subsidise A&P spend. SABMiller now has an opportunity to change all this. The focus of the revitalisation effort is to re-establish the core of the customer value proposition the brand lost and fundamentally rethink the business model.
The comparison with Corona is instructive. Corona sits at the other end of the spectrum with a growing 1.5% of global beer market volume (#4 brand globally). In 2011, the brand generated ~€0.5bn of EBIT, almost half of Modelo’s total at a 25% EBIT margin, a level of profitability on par with the soft drink giants. It has consistent pricing (upper-premium or lower super-premium), very few SKUs, a consistent and clearly differentiated pack type, special consumption style (with lime) and “Mexican-ness.” Unlike Foster’s, Corona is very strong and profitable in its home market and has one clear global RTM through its leading export team.
What went right?
Corona built a unique export business model based on its customer proposition. Outside Mexico and the US, Modelo participates in small, specific and highly profitable on-trade segments where it controls a niche position. The result has been small but sustainably strong and profitable market shares in over 30 global markets and throughout Modelo has stayed true to the core strengths of the brand’s business model to drive profitable growth.
Exercise 2:
Identify the unique customer proposition and right business model to support it.
- Develop a short-list of your brands with the potential to become global.
- Build a matrix listing key characteristics (e.g., positioning, image, packaging) and assess whether they have the potential of a unique proposition.
- Build a global consumer map with major needs-based segments on it.
- Position your selected brands onto the consumer map.
- Assess the overlap and prioritise those brands you believe have the greatest potential (i.e., “accessible headroom for profitable growth”).
- Place the competitor brands you believe have a global footprint or unique value proposition onto the map (these can be other beverage brands).
- Assess the gaps and overlap; what is the unique position for your brands?
- Select the brand with the right proposition and the least competition.
Consider the business model that will allow you to reach the right occasion or right consumer type (i.e., distributor model choice, outlet choice, sales team) and your desired price (i.e., through marketing mix, efficient supply chain, production agreements).
|
Step 3: Make space for your brand by repositioning your portfolio and build a detailed strategic plan
We discovered that companies that build global brands are able to reposition their portfolios effectively to foster new growth. This involves being clear on the value proposition of each brand, understanding where your global brand fits in the local portfolio and then creating a clear space in the consumers mind for it by repositioning existing brands. Repositioning should link back to achieving a consistent global image (see Figure 7). Finally it is important to note that short-term business unit financial targets may need to be recalibrated to allow for the required investments in successfully launching a global brand locally.
Figure 7: Repositioning brands
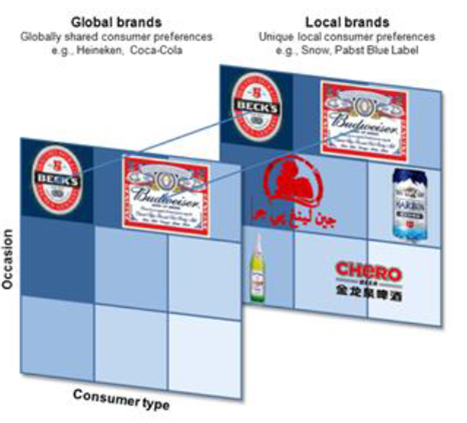
Harbin, a brewer in the northeast of China, was acquired by ABI in 2004. It had an extensive portfolio of local and regional brands, and through Harbin’s distribution network, ABI planned to launch its own brands, including Budweiser and Beck’s. Before launching, the ABI team conducted a simple consumer mapping analysis. Out of Harbin’s portfolio of approximately 100 brands, 30 were found to be unnecessary or overlapping and easily substitutable with different brands in the portfolio. These were generally money-losing brands and were either removed or their SKUs consolidated, and a clear space was created for both Beck’s and Bud in the brewer’s portfolio.
The topic of portfolio rationalization has always been a taboo in the industry. We have seen select brewers like ABI pursue this strategy with great effect, but the complexity of brand portfolios and consumer preferences in some markets implies higher execution risk, so it is not for all companies. We expect this to change slowly as the push toward global brands and hiring consumer goods talent in beer companies continues.
Building a strategic plan for your brand
After having reflected on where to position your brand within your portfolio, it is critical to go through a detailed exercise of strategic planning for your brand.
This exercise needs to cover the following key points:
- Definition of winning: what is the brand ambition, what are the objectives and key milestones over time
- Where to win: elaboration of accessible headroom in key target markets and channels
- How to win: reiteration of consumer positioning and unique value proposition (e.g., who is the consumer, role, functional/emotional benefits of the brand to the consumer, brand personality), key components of the business model and how they may vary across key markets (e.g., marketing mix strategy: communication, activation, innovation, pricing, route-to-market strategy, etc.)
Exercise 3:
Create space for your new brand by repositioning your portfolio. Build a local consumer map with the same axis as your global consumer map:
- Place your global brand onto your local consumer map.
- Reposition the local brands that are currently overlapping with your global brand.
- Place your competitor brands onto the consumer map and assess the overlap; do you need to change your strategy to take share from your competitors?
- Develop the strategic plan for your brand
|
Step 4: Build sustained success through long-term management and unambiguous centralised governance
Building global brands requires a long-term commitment with unwavering support across the organisation. We believe the good governance of successful brands shares six common approaches:
- Global brands take a long time to build, so organisations need to take a long-term perspective, which requires vision, belief and commitment. The rise of Blue Moon is often described as a “15-year overnight success story.” Despite Blue Moon’s deep consumer insight, disciplined management and commitment to a long-term vision, it still took more than a decade to gain a stable foothold as a niche player in the US beer market.
- Global brands need momentum as they build, so organisations need to choose the right markets to grow in, based on grounded facts rather than internal politics. Stella Artois, for example, only focuses on six key markets outside Western Europe and then seeds growth in key global cities.
- Global brands need consistency, so organisations need to be firm and clear that packaging, advertising, positioning and image are aligned across consumer maps and geographies at the same time as being open to valid input from the local teams and adjusting strategy accordingly. For instance, Carlsberg is re-igniting their brand using the “That calls for a Carlsberg” campaign in 140 markets although they are retaining their former positioning where it currently works best.
- Global brands require sustained investment but not at the expense of smart business decisions, so there should be a balance between finance, brand, strategy and local accountability to ensure the right resource allocation decisions are made. For example, Modelo has managed to invest heavily in building the Corona brand globally while at the same time expanding the Modelo brand in Mexico and the United States.
- Global brands must be governed globally with local execution and require a strong central team with singular overall accountability deciding on all matters such as the overall strategic plan and priorities, brand identity and key investment priorities. Clear accountabilities and responsibilities between central control and local execution is a tightrope, and good communication is essential. ABI has clearly accountable functions at both the centre and within business units. Individuals are solely responsible for the P&Ls of their country, which promotes local initiatives, but they are bound by the controls at the centre.
Exercise 4:
Build sustained success through long-term management and unambiguous centralised governance.
Assess your current practices and governance model:
- Are you managing your global brands for long-term success or with a short-term lens?
- Across the other six dimensions above, rate yourself on what are you currently doing well and what you could do better.
- Build a new governance plan and implement it.
|
In summary, the four steps of how to build a global beer brand are:
- Define the benefits of global brands to your organisation.
- Identify the unique proposition and build a business model to support it.
- Make space for your brand by repositioning your portfolio and build a detailed strategic plan.
- Build sustained success through long-term management and unambiguous centralised governance.
Freddy Heineken was a unique entrepreneur and, despite his limited formal marketing training, created the foundations for a top global brand, which was skilfully expanded by his successors. What is remarkable is that his success in the 60s and 70s has been successfully replicated only a few times since. Today, most international brewers have identified global brands as a key growth platform for the future. Stella is reclaiming ground in the UK following substantial investment, gaining traction fast in Argentina and making a strong global push through key cities. Carlsberg is investing in a global repositioning in 140 markets and looking to double profits by 2015. Heineken is committed to further accelerate Heineken’s international premium leadership and to pushing Desperados to global status.
There will be successes and failures. We believe that the companies that follow these four steps will set the stage for building brands that will be jewels in their crowns for years to come.